| 5 | Operations on Lists |
There are thousands of functions in the Wolfram Language that work with lists.
You can do arithmetic with lists:
In[1]:=
Out[1]=
In[2]:=
Out[2]=
Compute the first 10 squares:
In[3]:=
Out[3]=
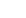
Plot the first 20 squares:
In[4]:=
Out[4]=

Sort sorts a list into order:
In[5]:=
Out[5]=
Length finds how long a list is:
In[6]:=
Out[6]=
Total gives the total from adding up a list:
In[7]:=
Out[7]=
Find the total of the numbers from 1 to 10:
In[8]:=
Out[8]=
Count counts the number of times something appears in a list.
Count the number of times a appears in the list:
In[9]:=
Out[9]=
It’s often useful to be able to get individual elements of a list. First gives the first element; Last gives the last element. Part gives the element at a particular position.
Pick out the first element of a list:
In[10]:=
Out[10]=
Pick out the last element:
In[11]:=
Out[11]=
Pick out element number 2:
In[12]:=
Out[12]=
Picking out the first element in a list you’ve sorted is the same as finding the minimum element:
In[13]:=
Out[13]=
In[14]:=
Out[14]=
If you have a number, like 5671, you can make a list of its digits using IntegerDigits[5671].
Break a number into a list of digits:
In[15]:=
Out[15]=
Find the last digit:
In[16]:=
Out[16]=
Take lets you take a specified number of elements from the beginning of a list.
Take the first 3 elements from a list:
In[17]:=
Out[17]=
Take the first 10 digits of 2 to the power 100:
In[18]:=
Out[18]=
Drop drops elements from the beginning of a list.
In[19]:=
Out[19]=
| {2,3,4}+{5,6,2} | arithmetic on lists | |
| Sort[{5,7,1}] | sort a list into order | |
| Length[{3,3}] | length of a list (number of elements) | |
| Total[{1,1,2}] | total of all elements in a list | |
| Count[{3,2,3},3] | count occurrences of an element | |
| First[{2,3}] | first element in a list | |
| Last[{6,7,8}] | last element in a list | |
| Part[{3,1,4},2] | particular part of a list, also written as {3, 1, 4}[[2]] | |
| Take[{6,4,3,1},2] | take elements from the beginning of a list | |
| Drop[{6,4,3,1},2] | drop elements from the beginning of a list | |
| IntegerDigits[1234] | list of digits in a number |
5.1Make a list of the first 10 squares, in reverse order. »
5.2Find the total of the first 10 squares. »
5.3Make a plot of the first 10 squares, starting at 1. »
5.6Make a combined list of the first 5 squares and cubes (numbers raised to the power 3), sorted into order. »
5.7Find the number of digits in 2^128. »
5.8Find the first digit of 2^32. »
5.9Find the first 10 digits in 2^100. »
5.10Find the largest digit that appears in 2^20. »
5.11Find how many zeros appear in the digits of 2^1000. »
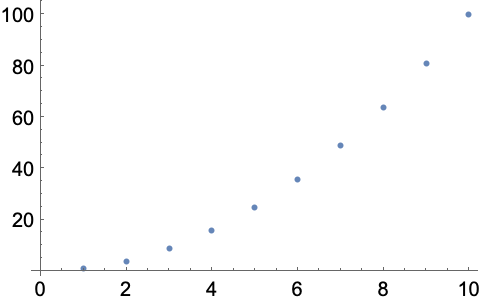
5.13Make a line plot of the sequence of digits that appear in 2^128. »
+5.1Make a list of the first 10 multiples of 3. »
+5.3Find the last digit of 2^37. »
+5.4Find the second-to-last digit of 2^32. »
+5.5Find the sum of all the digits of 3^126. »
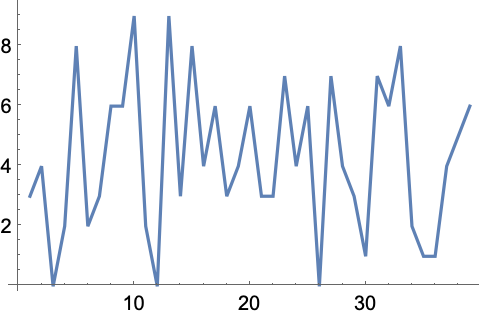
+5.6Make a pie chart of the sequence of digits that appear in 2^32. »
+5.7Make a list of pie charts for the sequence of digits in 2^20, 2^40, 2^60. »
Can one add lists of different lengths?
Can there be a list with nothing in it?
Yes. {} is a list of length 0, with no elements. It’s usually called the null list or the empty list.
- IntegerDigits[5671] gives digits in base 10. IntegerDigits[5671, 2] gives digits in base 2. You can use any base you want. FromDigits[{5, 6, 7, 1}] reconstructs a number from its list of digits.
- Rest[list] gives all the elements of list after the first one. Most[list] gives all elements other than the last one.