Vektoranalysis & -visualisierung
In der Wolfram Language werden n-dimensionale Vektoren durch Listen der Länge n dargestellt.
Berechne das Skalarprodukt aus zwei Vektoren:
| Out[1]= | 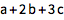 |
Gib ESCcrossESC für das Kreuzprodukt-Symbol ein:
| Out[2]= | 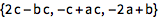 |
Berechne die Norm eines Vektors:
Ermittle die Projektion eines Vektors auf der x-Achse:
Ermittle den Winkel zwischen zwei Vektoren:
Berechne den Gradient eines Vektor:
(Für das ∇-Symbol, gib ESCgradESC ein.)
| Out[1]= | 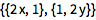 |
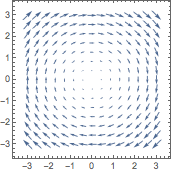
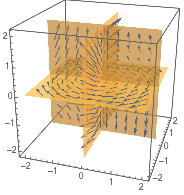
Berechne die Divergenz oder Rotation eines Vektorfelds:
| Out[2]= |  |