생체 구조를 동상으로 변환
인간 생체 구조의 고해상도 3D 모델에 Wolfram 언어의 강력한 그래픽과 공간 처리 기능을 더하여 프로그램적으로 인체를 모델을 기반으로 하는 현대적 조각으로의 구축이 가능합니다.
다음 Antony Gormley의 몇몇 작품을 감상해 봅니다. (http://www.antonygormley.com/sculpture/chronology).
전체 Wolfram 언어 입력 표시하기
In[1]:=
WikipediaData["Antony Gormley", "ImageList"] //
Select[#,
Length[Union[#]]/Length[#] &[ImageData[#][[1, 1]]] > 0.8 &] &Out[1]=

인체를 충실히 표현한 작품을 로드합니다.
In[2]:=
human = AnatomyData[Entity["AnatomicalStructure", "Skin"],
"MeshRegion"]Out[2]=

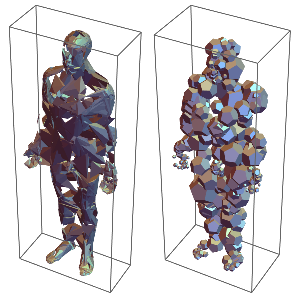
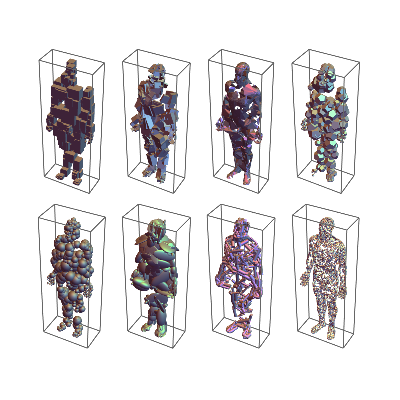
다양한 영역 함수를 사용하여 다양한 종류의 동상을 쉽게 만들 수 있습니다.
전체 Wolfram 언어 입력 표시하기
In[3]:=

pts = MeshCoordinates[human];
nf = Nearest[pts];
color := Directive[GrayLevel[RandomReal[{0.5, 0.7}]],
Specularity[RandomColor[], RandomInteger[{10, 20}]]]In[4]:=

With[{dode = N[PolyhedronData["Dodecahedron"][[1]]]},
ballToDodecahedron[Ball[p_, r_]] :=
Translate[
Scale[Rotate[dode, RandomReal[{-Pi, Pi}],
RandomReal[{-1, 1}, 3], {0, 0, 0}], r], p]]In[5]:=

GraphicsGrid[
Partition[#,
4] &@{Graphics3D[{EdgeForm[], color,
Table[BoundingRegion[
nf[RandomChoice[pts], RandomInteger[{100, 1000}]],
"MinCuboid"], {200}]}],
Graphics3D[{EdgeForm[], color,
Table[BoundingRegion[
nf[RandomChoice[pts], RandomInteger[{100, 1000}]],
"FastOrientedCuboid"], {250}]}],
Graphics3D[{color, EdgeForm[],
Table[Show[
BoundingRegion[
RandomChoice[
nf[RandomChoice[pts], RandomInteger[{100, 2000}]],
RandomInteger[{4, 12}]], "MinConvexPolyhedron"]][[
1]] /. _Directive :> {}, {600}]}],
Graphics3D[{color, EdgeForm[],
Table[ballToDodecahedron@
BoundingRegion[
RandomChoice[nf[RandomChoice[pts], RandomInteger[{100, 600}]],
RandomInteger[{4, 12}]], "FastBall"], {300}]}],
Graphics3D[{color,
Table[BoundingRegion[
RandomChoice[
nf[RandomChoice[pts], RandomInteger[{100, 600}]],
RandomInteger[{4, 12}]], "FastBall"], {500}]}],
Graphics3D[{color,
Table[
BoundingRegion[
RandomChoice[nf[RandomChoice[pts], RandomInteger[{100, 2000}]],
RandomInteger[{4, 12}]], "FastEllipsoid"], {350}]}],
Graphics3D[{color, EdgeForm[],
Table[Cylinder[{#, nf[#, RandomInteger[{2000, 5000}]][[-1]]} &[
RandomChoice[pts]],
RandomReal[{5, 25}]], {600}]}],
Module[{pts2 = RandomSample[pts, 6000], nf2},
nf2 = Nearest[pts];
Graphics3D[{color, EdgeForm[], CapForm["Round"],
Cylinder[{#, nf2[#, 100][[-1]]}, 6] & /@
RandomSample[pts2]}]]}, Spacings -> {-150, Automatic},
ImageSize -> Full
] // Rasterize[#, "Image", ImageSize -> {400, 400}] &Out[5]=
회전과 함께 다리와 팔 부분을 잡아 늘이는 변환을 적용하여 천사와 같은 형태의 동상을 만들어 더 고전적인 외관의 작품도 생성할 수 있습니다.
전체 Wolfram 언어 입력 표시하기
In[6]:=

nonlinearTransform3D[expr_, g_] :=
Module[{gD, inv, newNormal, newVertices, newNormals},
gD[x_, y_, z_] =
Compile[{x, y, z}, Evaluate[D[g[{x, y, z}], {{x, y, z}}]]];
inv[m_] :=
With[{im = Inverse[m]},
If[Head[im] === Inverse, m, PseudoInverse[m]]];
newNormal[{vertex_, normal_}] :=
Quiet[With[{m = inv[Transpose[gD[vertex]]]},
If[Sign[Det[m]] == -1, -1, 1] m.normal]];
expr /. {GraphicsComplex[vertices_, body_, a___,
VertexNormals -> normals_,
b___] :> (newVertices = g /@ vertices;
newNormals = newNormal /@ Transpose[{vertices, normals}];
GraphicsComplex[newVertices, body, a,
VertexNormals -> newNormals, b])}]In[7]:=

doubleTwist[{x_, y_, z_}] :=
With[{h = 1000, w = 180, H = 1300, \[Xi] = 600, \[Kappa] = 150},
With[{\[CurlyPhi] =
6 Pi If[z > h || (z > \[Xi] && Sqrt[x^2] > w), 0,
Cos[Pi/2 (h - z)/h]],
\[CurlyTheta] = -1.6 Pi If[(z > \[Xi] && Sqrt[x^2] < w) ||
z < \[Xi], 0, Cos[Pi/2 (w - x)/w]],
f = Piecewise[{{1, z > h}, {1 + (h - z)/h, z < h}}],
g = If[(z > \[Xi] && Sqrt[x^2] < w) || z < \[Xi], 1,
1 + (Sqrt[x^2] - w)/\[Kappa]]}, {{g, 0, 0}, {0,
Cos[\[CurlyTheta]],
Sin[\[CurlyTheta]]}, {0, -Sin[\[CurlyTheta]],
Cos[\[CurlyTheta]]}}.({{f Cos[\[CurlyPhi]], f Sin[\[CurlyPhi]],
0}, {-f Sin[\[CurlyPhi]], f Cos[\[CurlyPhi]], 0}, {0, 0,
1}}.{x, y, z} - {0, 0, H}) + {0, 0, H}]]In[8]:=
smoothHuman = Entity["AnatomicalStructure", "Skin"]["Graphics3D"];In[9]:=
Show[nonlinearTransform3D[smoothHuman, doubleTwist],
ViewPoint -> {-1, -2, 0}, Method -> {"ShrinkWrap" -> True}]Out[9]=