分析、可视化和对比 “超级食物”
超级食品是一种或多种营养含量非常高的食品. 该范例定义了一组超级食品,然后与其他 Wolfram Knowledgebase 中更“普遍”的食品对比. 最终构建一个值得“超级”绰号的食品的图标.
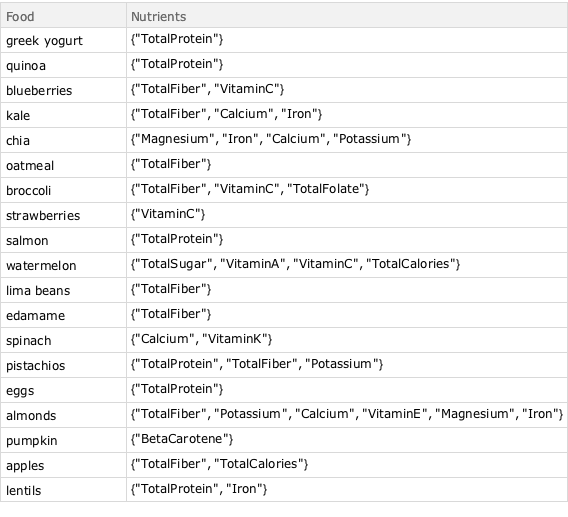
首先,定义一个包含已知营养成分的超级食物列表.
In[1]:=

superfoodsRawData = {{"greek yogurt", {"TotalProtein"}}, {"quinoa", \
{"TotalProtein"}}, {"blueberries", {"TotalFiber",
"VitaminC"}}, {"kale", {"TotalFiber", "Calcium",
"Iron"}}, {"chia", {"Magnesium", "Iron", "Calcium",
"Potassium"}}, {"oatmeal", {"TotalFiber"}}, {"broccoli", \
{"TotalFiber", "VitaminC",
"TotalFolate"}}, {"strawberries", {"VitaminC"}}, {"salmon", \
{"TotalProtein"}}, {"watermelon", {"TotalSugar", "VitaminA",
"VitaminC", "TotalCalories"}}, {"lima beans", {"TotalFiber"}},
{"edamame", {"TotalFiber"}}, {"spinach", {"Calcium",
"VitaminK"}}, {"pistachios", {"TotalProtein", "TotalFiber",
"Potassium"}}, {"eggs", {"TotalProtein"}}, {"almonds", \
{"TotalFiber", "Potassium", "Calcium", "VitaminE", "Magnesium",
"Iron"}}, {"pumpkin", {"BetaCarotene"}}, {"apples", \
{"TotalFiber", "TotalCalories"}}, {"lentils", {"TotalProtein",
"Iron"}}};将其转换至 Dataset 以便进行更简单对比.
In[2]:=
superfoodsDatset =
Dataset[<|"Food" -> #1, "Nutrients" -> #2|> & @@@ superfoodsRawData]Out[2]=
使用 Interpreter 获取关于超级食品的 Wolfram 语言实体.
In[3]:=

superfoodsDatset1 =
superfoodsDatset[All,
KeySort[Prepend[#, <|
"FoodEntity" -> Interpreter["Food"][#Food]|>]] &];列出营养成分.
In[4]:=
Union @@ Normal[superfoodsDatset1[[All, "Nutrients"]]]Out[4]=
设置将给定营养成分转换为合适属性的规则.
In[5]:=

superfoodsDatset2 =
superfoodsDatset1 /.
AssociationMap[
EntityProperty["Food", "Relative" <> # <> "Content"] &,
Union @@ Normal[superfoodsDatset1[[All, "Nutrients"]]]]Out[5]=

从 Dataset 中找出最常见营养成分.
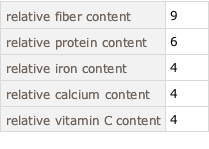
In[6]:=
mostCommonProperties =
superfoodsDatset2[Counts[Flatten[#]] &, "Nutrients"][TakeLargest[5]]Out[6]=
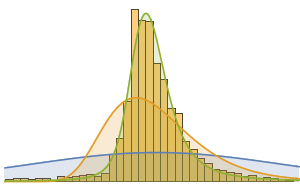
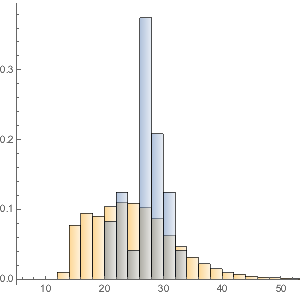
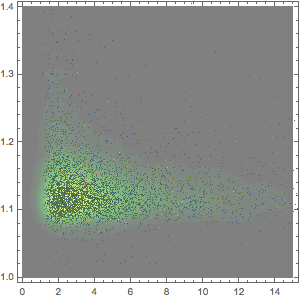
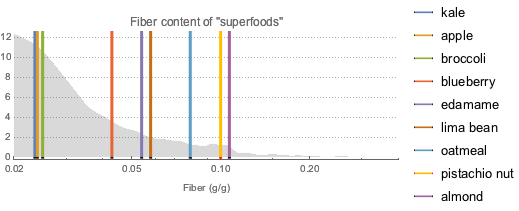
找出认为纤维含量高的超级食品,并与其他近 9,000 种食品进行比较. 在此,灰色曲线是大多数食品中纤维成分的概率密度函数.
In[7]:=

fiberDataset =
superfoodsDatset2[
Select[ContainsAny[#Nutrients, {EntityProperty["Food",
"RelativeTotalFiberContent"]}] &], KeyDrop["Nutrients"]];显示完整的 Wolfram 语言输入
Out[13]=
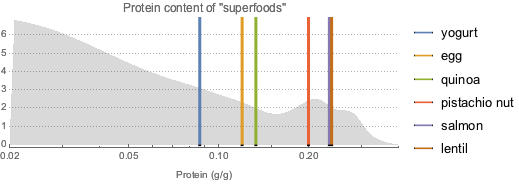
对高蛋白超级食品进行同样操作.
In[14]:=
proteinDataset =
superfoodsDatset2[
Select[ContainsAny[#Nutrients, {EntityProperty["Food",
"RelativeTotalProteinContent"]}] &], KeyDrop["Nutrients"]];显示完整的 Wolfram 语言输入
Out[21]=
创建超级食品图标,从一些超级食品图像开始.
In[22]:=

GraphicsGrid[
Partition[
ims = EntityValue[
Cases[superfoodsDatset2[All, "FoodEntity"] // Normal,
Entity["FoodType", _], Infinity], "Image"], UpTo[5]]]Out[22]=

作为背景,使用大家都知道的有超级含义的图形.
In[23]:=
Entity["Lamina", "SupermanInsigniaLamina"]["Image"] // ImageCropOut[23]=

使用简单的图像处理将其转换为背景.
In[24]:=

background =
ColorNegate[
Binarize[Entity["Lamina", "SupermanInsigniaLamina"]["Image"], .99]]Out[24]=

创建包含超级食品的“词汇云”.
In[25]:=
wc = WordCloud[(RandomReal[{0.6, 1.2}] -> #) & /@ ims, background]Out[25]=

将词汇云和背景组合.
In[26]:=
ImageMultiply[{ColorReplace[background, Black -> LightGray], wc}]Out[26]=