Herd Immunity
When a large percentage of the population becomes immune to a disease such as COVID-19, you can consider the population to be protected from the disease by herd immunity. This means that although 100% of the population may not be vaccinated, a sufficient proportion of the population is, and the rate of infection starts to decrease. In this virtual lab, you will investigate the concept of herd immunity using the SIR (susceptible, infected and recovered) model.
Model
The model used in this exercise is based on the SIR (susceptible, infected, recovered) model. This classical epidemiological model was developed by Kermack and McKendrick in the early 1900s and is one of the most well-known models for studying infectious diseases within populations. Since its development, there have been many adaptations of the model, allowing it to be used in a wide variety of settings and contexts.
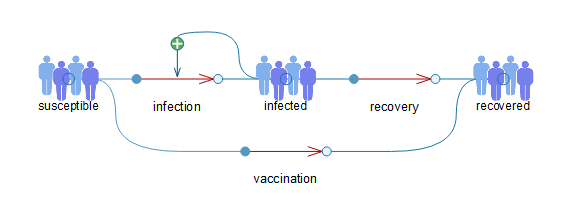
SIR model with vaccination.
Analysis
Analyze the impact of infection for different basic reproduction number (R0) values and mean infectious period. To model the influence of COVID-19, set the R0 value to 2.65 and the mean infectious period to 5 days.
Analysis
Use the Wolfram Language to carry out parametric analysis.
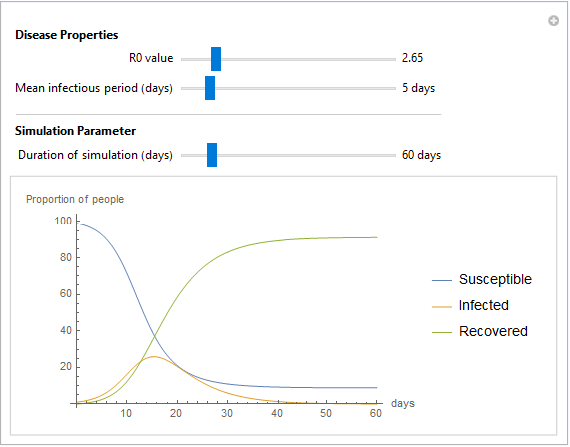
Dynamic visualization of spread of an infectious disease.
Wolfram System Modeler
Try
Buy
System Modeler is available in English
and Japanese
on Windows, macOS & Linux »
Questions? Comments? Contact a Wolfram expert »