利用内置数据改善精选数据集
Wolfram 知识库中丰富的内置社会经济学数据集合可以用于改善外部数据源.
从美国住房和城市发展部(HUD)导入 Head Start 机构的地址数据集,作为开始.
In[1]:=
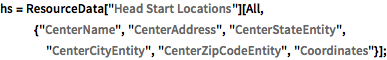
hs = ResourceData["Head Start Locations"][
All, {"CenterName", "CenterAddress", "CenterStateEntity",
"CenterCityEntity", "CenterZipCodeEntity", "Coordinates"}];In[2]:=
Take[hs, 5]Out[2]=
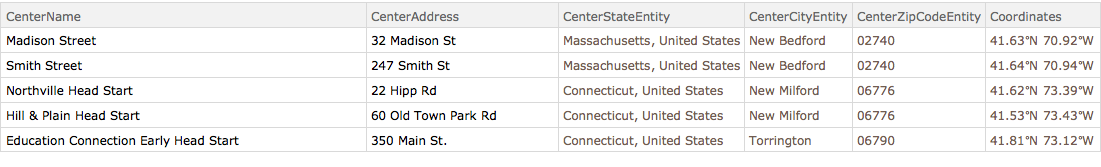
使用选择算符提取位置的一个子集.
In[3]:=
hsChicago =
hs[Select[#CenterCityEntity ===
Entity["City", {"Chicago", "Illinois", "UnitedStates"}] &]];将它们表示在芝加哥地图上.
In[4]:=
GeoListPlot[hsChicago[All, #Coordinates &]]Out[4]=
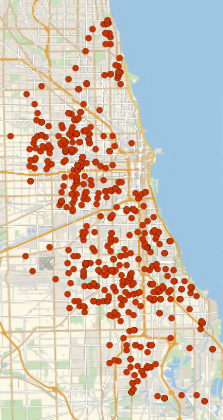
将 Head Start 地址分组,并根据邮政编码绘制它们的分布图.
In[5]:=
chicagoCounts = Length /@ GroupBy[hsChicago, #CenterZipCodeEntity &];In[6]:=
GeoRegionValuePlot[chicagoCounts]Out[6]=
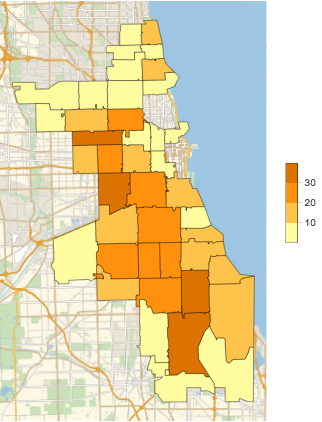
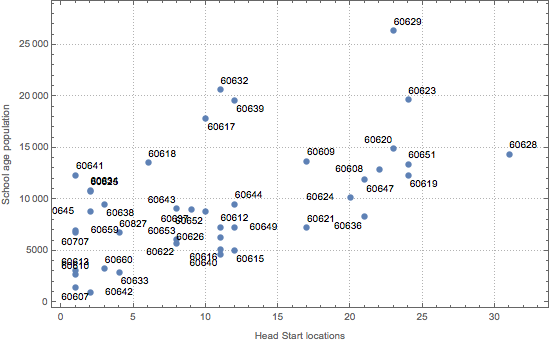
检索在芝加哥邮编代码内有关学龄人口的内置数据,并将这些值与从 HUD 外部数据推导的 Head Start 地址计数绘图.
In[7]:=
zipcodes = Normal@Keys[chicagoCounts]Out[7]=

In[8]:=

chicagoMedian =
EntityValue[zipcodes,
EntityProperty["ZIPCode", "Population", {"Age" -> "SchoolAge"}],
"EntityAssociation"];显示完整的 Wolfram 语言输入
Out[9]=