PCB構造を列挙し,実体ストアを通して共有する
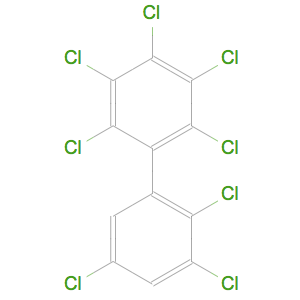
ポリ塩化ビフェニル(PCB)は,化学式が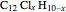 で与えられる有機化合物である.PCBは,変圧器を含む数多くの工業的応用に使用されてきた.ここでは,可能なすべてのPCBを生成し,それをカスタム実体として実体ストアに保存するプロセスを説明する.
で与えられる有機化合物である.PCBは,変圧器を含む数多くの工業的応用に使用されてきた.ここでは,可能なすべてのPCBを生成し,それをカスタム実体として実体ストアに保存するプロセスを説明する.
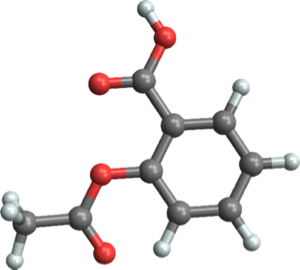
ChemicalDataには,すでにPCBの骨格,ジフェニル(しばしばビフェニルとも呼ばれる)が含まれている.
Entity["Chemical", "Biphenyl"]["ColorStructureDiagram"]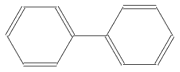
ChemicalDataには,PCB分子の特定の同族元素も含まれている.
Entity["Chemical", "PCB"][
EntityProperty["Chemical", "ColorStructureDiagram"]]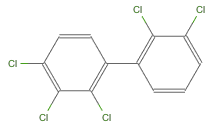
PCBの一般的な構造は,以下に「X」で示してあるように,10の位置が含まれている.一塩素化体から十塩素化体までの可能なすべての塩素化誘導体(つまり同族体)を得るためにし,上記の10のロカントに可能なすべての方法で塩素置換基を付ける.ここでは,"MOL"形式表現として包括的構造が定義済みのCloudObjectからロードされる.

molString = CloudGet[CloudObject[
"https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/user-722de5bb-ef39-4cbd-\
999d-546c888892d6/PCB_scaffold"]][[2]];ImportString[molString, "MOL"]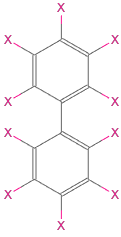
基本的な群論によって,すべてのPCB構造を列挙することができる.置換群として表現された骨格全体の本質的な対称特性が出発点となる.

biphenylSymmetry =
PermutationGroup[{Cycles[{{6, 10}, {7, 9}}],
Cycles[{{1, 5}, {2, 4}}],
Cycles[{{1, 6}, {2, 7}, {3, 8}, {4, 9}, {5, 10}}]}];Pólyaの計数定理からサイクル指標多項式を形成し,その係数を操作して210の同族元素(塩素を含まないためにPCBとはみなされない,置換されていない炭化水素構造を含む)を取得する.
ci = Factor[
CycleIndexPolynomial[biphenylSymmetry, Array[Subscript[x, #] &, 4]]]Total[CoefficientList[Expand[ci /. Subscript[x, i_] -> (x^i + 1)], x]]簡単な文字列置換を使ってロカント位置の名前を変更した後,全部で209個のIUPAC準拠の名前が生成される.

conPos = Flatten[(PositionIndex /@
First /@
GroupOrbits[biphenylSymmetry, Permutations[#],
Permute]) & /@ (LowerTriangularize[
ConstantArray["Cl", {10, 10}]] /. 0 -> "H")] /.
Thread[Range[10] -> {"2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "2'", "3'", "4'",
"5'", "6'"}];
(names = Flatten[{StringJoin[Riffle[Sort[#["Cl"]], ","]] <>
"-" <> (Length[#["Cl"]] /.
Thread[Range[10] -> {"Chloro", "Dichloro", "Trichloro",
"Tetrachloro", "Pentachloro", "Hexachloro",
"Heptachloro", "Octachloro", "Nonachloro",
"Decachloro"}]) <> "biphenyl"} & /@ conPos] /.
"2,2',3,3',4,4',5,5',6,6'-Decachlorobiphenyl" ->
"Decachlorobiphenyl") // Short同様の方法で,すべての同族元素構造の生成を行うことができる.

PCBstruct =
ImportString[
StringReplacePart[molString, #, StringPosition[molString, "X"]],
"MOL"] & /@
Flatten[(First /@
GroupOrbits[biphenylSymmetry, Permutations[#],
Permute]) & /@ (LowerTriangularize[
ConstantArray["Cl", {10, 10}]] /. 0 -> "H"), 1];TextGrid[Transpose[{names, PCBstruct}] // Take[#, 2] &,
Dividers -> All]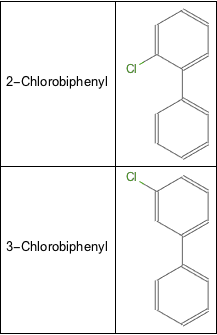
同族元素のより詳細な特性を含めたければ,計算済みのCloudObjectからPCBをデータ集合としてインポートするとよい.
imp = CloudGet[CloudObject[
"https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/user-722de5bb-ef39-4cbd-\
999d-546c888892d6/PCB_congeners_propertylist"]]; TextGrid[Take[imp, 5], Background -> {Automatic, {LightBlue}},
Dividers -> All]
インポートしたデータを先ほど計算した構造および名前と組み合せる.

TextGrid[(PCBdata =
SortBy[MapThread[
Flatten[{#1,
Pick[imp[[3 ;;]], imp[[3 ;;, 1]], #2]}] &, {PCBstruct,
names}], #[[3]] &]) // Take[#, 2] &, Dividers -> All]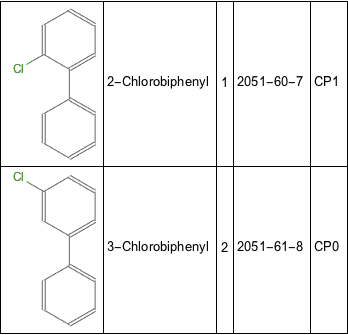
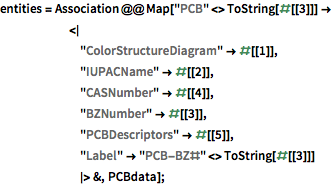
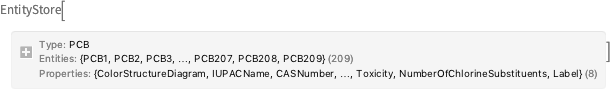
これらのPCB構造についてのカスタム実体ストアを作る.

store = EntityStore[
"PCB" -> <|
"Label" -> "polychlorinated biphenyl",
"LabelPlural" -> "polychlorinated biphenyls",
"Entities" -> entities,
"Properties" -> properties,
"EntityClasses" -> classes
|>]
このセッション用にストアを登録する.
PrependTo[$EntityStores, store];ランダム実体を呼び出すことで実体ストアを試す.
EntityValue[RandomEntity["PCB"], "PropertyAssociation"]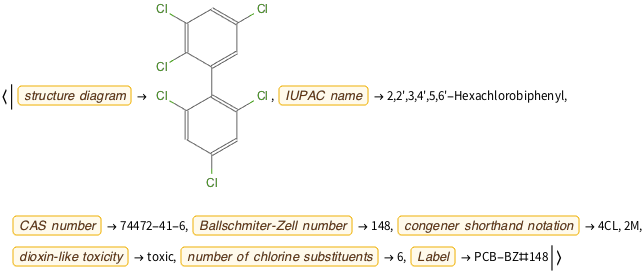
すべてのカスタム実体が今後のセッションあるいは公開アプリで使えるように,実体ストアをCloudObjectに書き込む.
CloudPut[store, "PCB_entity_store", Permissions -> "Public"]