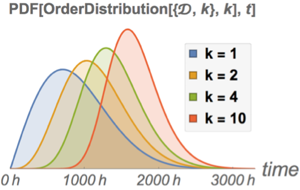
数量を含む切断分布
アメリカのクランベリーの直径は,平均16mm,標準偏差1.6mmの正規分布に従う.果実は,直径が少なくとも15mmなければ,丸ごとの形で売ることはできない.それ以外のサイズのものはクランベリーソースの生産に使われる.丸ごとの形で売られる果実のサイズの分布を求める.
In[1]:=
cran\[ScriptCapitalD] =
NormalDistribution[Quantity[16, "Millimeters"],
Quantity[1.6, "Millimeters"]];
\[ScriptCapitalD] =
TruncatedDistribution[{Quantity[15, "Millimeters"], \[Infinity]},
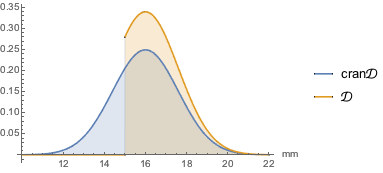
cran\[ScriptCapitalD]];確率密度関数を比べる.
In[2]:=

Plot[{PDF[cran\[ScriptCapitalD], Quantity[x, "Milimeters"]],
PDF[\[ScriptCapitalD], Quantity[x, "Milimeters"]]}, {x, 10, 22},
PlotLegends -> {"cran\[ScriptCapitalD]", "\[ScriptCapitalD]"},
Filling -> Axis, AxesLabel -> {"mm"}]Out[2]=
1ポンドパッケージのクランベリーは,容量がおよそ30立方インチであるとして,そのようなパッケージに入っているクランベリーの数の上限と下限それぞれの平均を求める.
In[3]:=

lowerbound =
Floor[NExpectation[
Divide[Quantity[30, "Inches"^3],
Volume[Cuboid[{0, 0, 0}, {x, x, x}]]],
x \[Distributed] \[ScriptCapitalD]]]Out[3]=
In[4]:=

upperbound =
Ceiling[NExpectation[
Divide[Quantity[30, "Inches"^3], Volume[Ball[{0, 0, 0}, x/2]]],
x \[Distributed] \[ScriptCapitalD]]]Out[4]=