Measuring Car Velocity via Acoustic Doppler Effect
Velocity measurement can be done by fitting a Doppler model to the measured change in frequencies extracted from a sound sample.
Sound sample of a Doppler effect.
| In[1]:= | 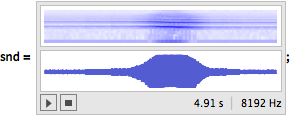 X |
| In[2]:= | X |
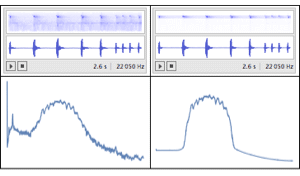
Apply a continuous wavelet transformation with a Gabor wavelet.
| In[3]:= | X |
| In[4]:= | X |
| Out[4]= | 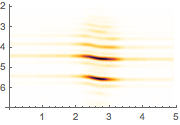 |
Antialiased subsampling of the wavelet data to 32Hz.
| In[5]:= | X |
| In[6]:= |  X |
Measure the scale shift via correlation.
| In[7]:= | 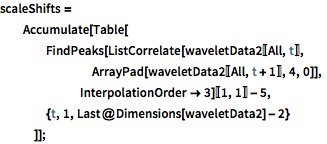 X |
Convert shifts in wavelet scale back to change in frequency.
| In[8]:= | X |
| In[9]:= | X |
| In[10]:= | X |
| Out[10]= | 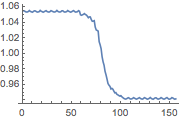 |
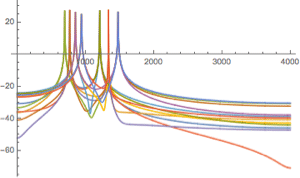
Fit Doppler model to measured change in frequency.
| In[11]:= |  X |
| Out[11]= | 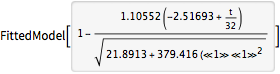 |
| In[12]:= | X |
| Out[12]= | 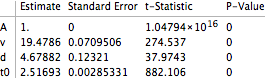 |
Result: car speed = 19.5 m/s minimum distance = 4.7m
| In[13]:= | X |
| Out[13]= |