Compute Measures (Length, Area, Volume, etc.)
The measure of a region corresponds to length of a curve, area of a surface, and volume of a solid. But it also generalizes to zero-dimensional objects where the measure is counted, as well as  -dimensional objects where the measure is a generalized volume. For a region containing parts with different dimensions, the measure is taken to be the one that corresponds to the maximal dimension, and the measure is given by the integral
-dimensional objects where the measure is a generalized volume. For a region containing parts with different dimensions, the measure is taken to be the one that corresponds to the maximal dimension, and the measure is given by the integral 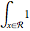 , where
, where 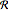 is the region.
is the region.
Curve lengths.
| In[1]:= | X |
| Out[1]= |
| In[2]:= | X |
| Out[2]= |
| In[3]:= | X |
| Out[3]= |
| In[4]:= | X |
| Out[4]= |
| In[5]:= |  X |
| Out[5]= |
Surface areas.
| In[6]:= | X |
| Out[6]= |
| In[7]:= | X |
| Out[7]= |
| In[8]:= | X |
| Out[8]= |
| In[9]:= | X |
| Out[9]= |
| In[10]:= |  X |
| Out[10]= |
Solid volumes.
| In[11]:= | X |
| Out[11]= |
| In[12]:= | X |
| Out[12]= |
| In[13]:= | X |
| Out[13]= |
| In[14]:= | 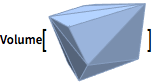 X |
| Out[14]= |
General  -dimensional measures for unit spheres, balls, and simplices.
-dimensional measures for unit spheres, balls, and simplices.
| In[15]:= | X |
| Out[15]= |
| In[16]:= | X |
| Out[16]= |
| In[17]:= | X |
| Out[17]= |
| In[18]:= | X |
| Out[18]= |
| In[19]:= | X |
| Out[19]= |
| In[20]:= | X |
| Out[20]= |