WolframAstronomyA Core Part of
Wolfram Language
Compute and Visualize Astronomical Data.
Make astronomy computable with curated astronomical data and precise positional information obtained from the latest available ephemerides. Easily create detailed maps of the sky and visualize astronomical events from the past or future.
Astro Computation
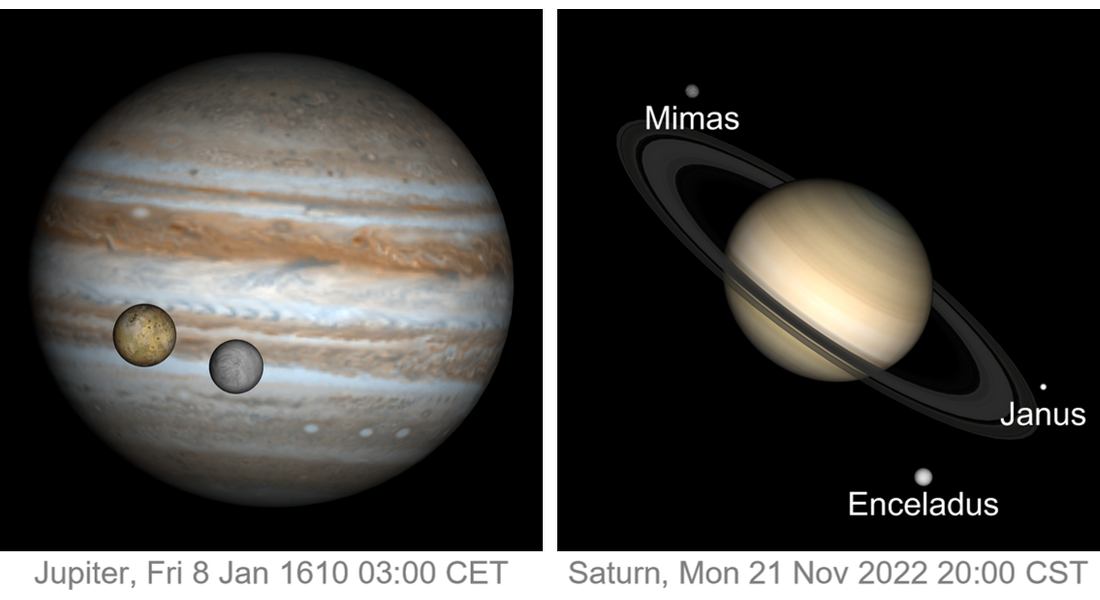
Find distances, angular separations and timings for any astronomical event from stars, galaxies and black holes to objects near the Earth. Compute the positions of millions of astronomical objects as seen from different observation locations and times.
Precise Solar System Dynamics
Compute the position of planets, moons, asteroids and comets for precise timing of historic and future events. Starting from precise JPL ephemerides, use any type of frame or coordinate system, include refraction corrections or relativistic effects, and more.
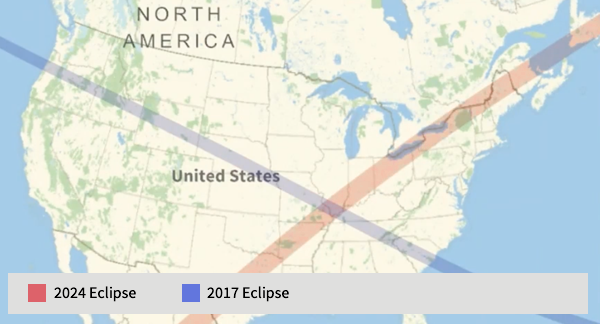
Eclipses
Compute properties of solar and lunar eclipses and visualize them with precise maps of the sky or ground track. Predict and explore eclipse circumstances from the far past to the far future with high‐precision computations for the Sun, Moon and Earth.
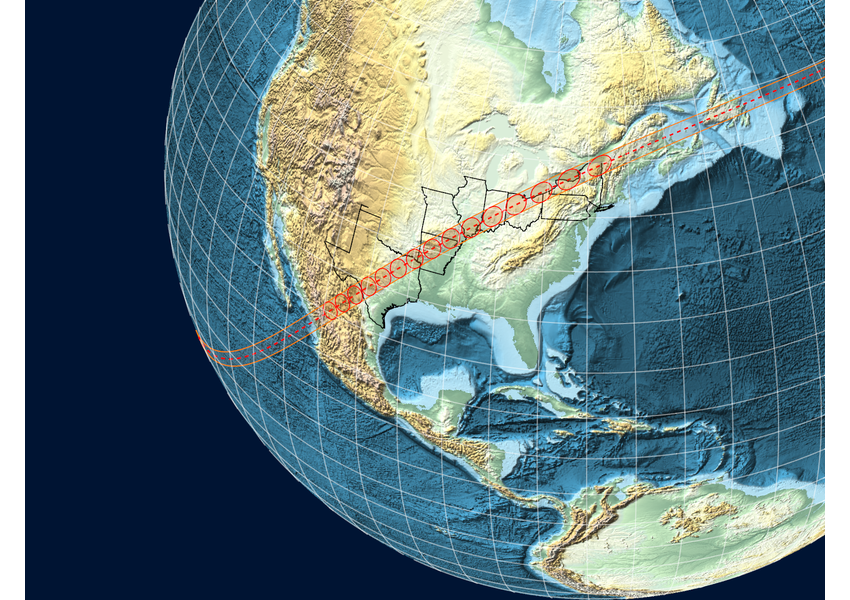
Astro Formulas
Explore fundamental formulas for computing astronomical phenomena from simple observational concepts like brightness to modern astrophysical properties of black holes. Use advanced typesetting to present those formulas and find results.
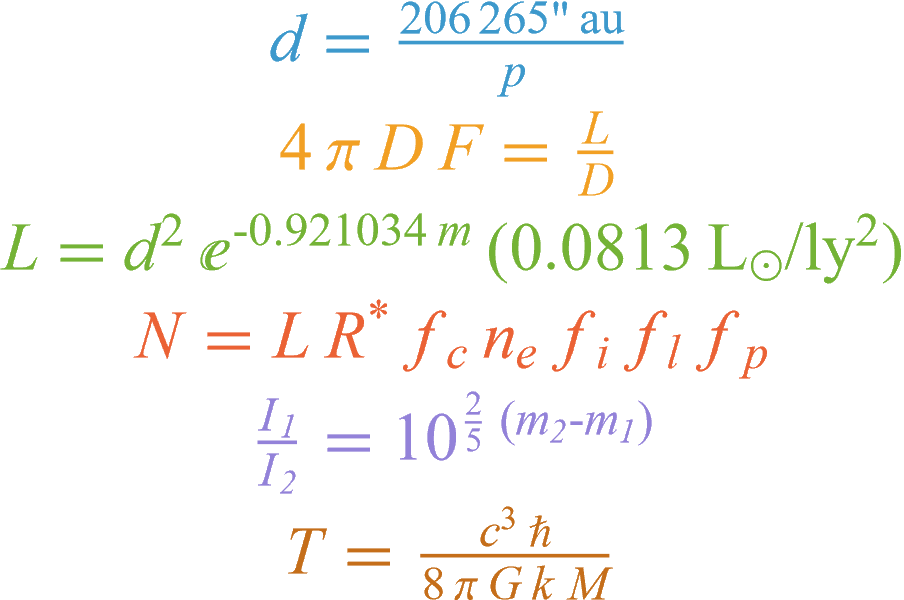
Astro Data
Query for curated data on millions of astronomical entities such as planets, spacecraft and nebulas and combine it with your own imported data in formats such as FITS, JSON and CSV to perform analyses and gain insight.
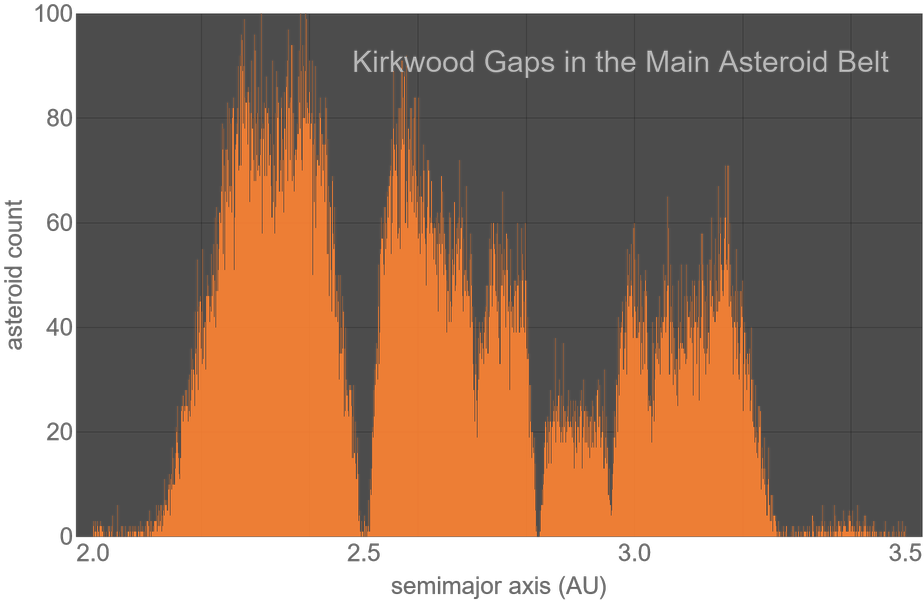
Astro Visualization
Visualize astronomical scenes in different map projections. Choose simple colored backgrounds or use photorealistic ones to give context to precise astronomical positions, whether manually specified or calculated for any location and date.
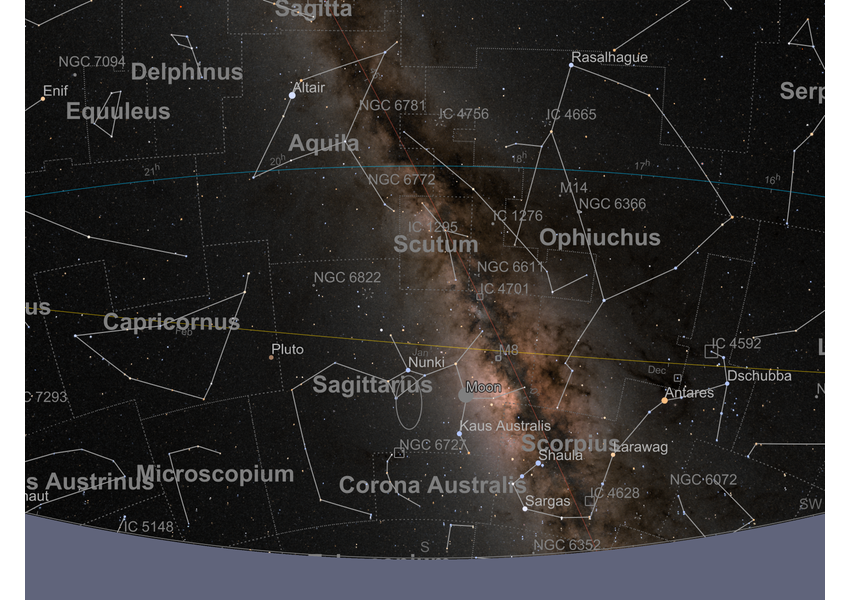
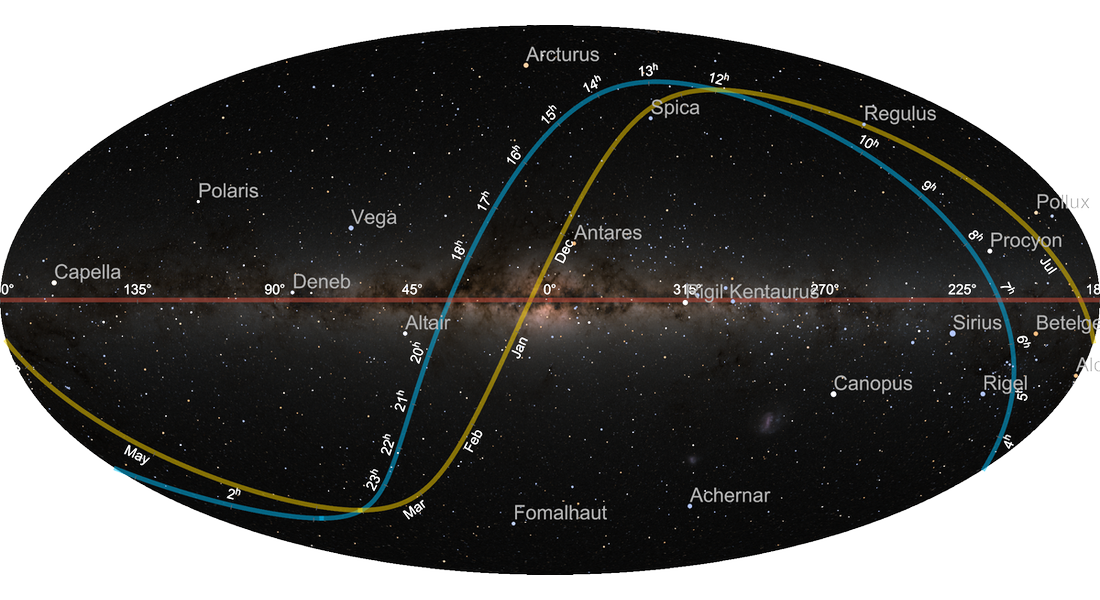
Constellations and Star Maps
Create highly stylized star maps with constellation boundaries, stick figures and artistic illustrations to provide positional context for astronomical objects. Use standard data on all 88 official International Astronomical Union constellation boundaries.
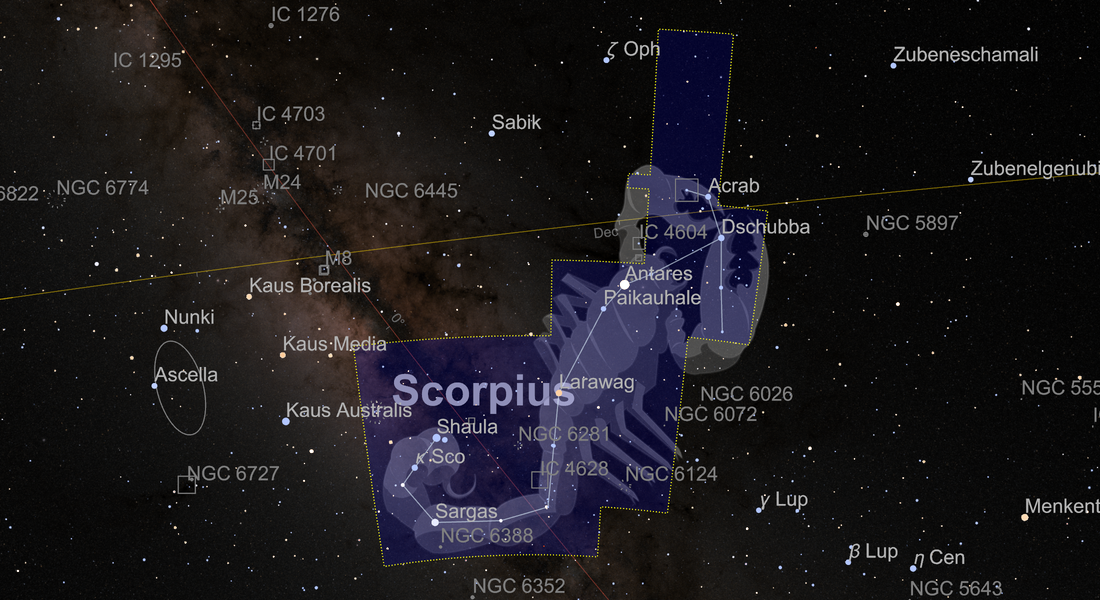
Time in Astronomy
Compute and visualize astronomical events at future and past dates. Use a symbolic representation of dates, times, time zones, calendars and time systems, including control of leap seconds, for all time granularities from years to nanoseconds.
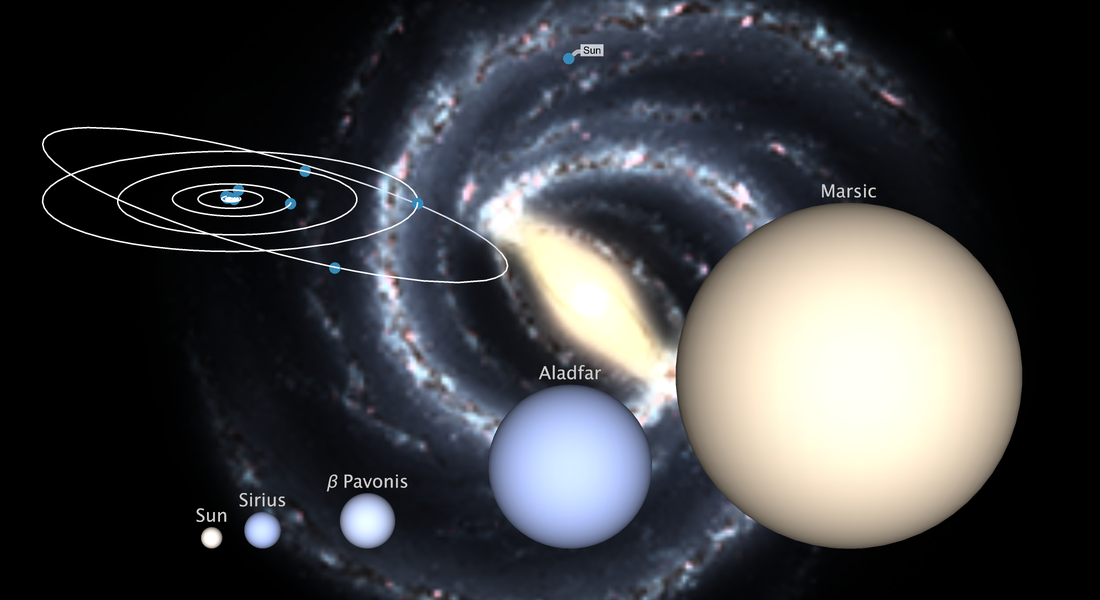
Scales in the Universe
From Planck scales to the largest scales in the universe, annotate your data with a complete collection of units to attach physical meaning to raw numbers, perform dimensional analysis and convert units.
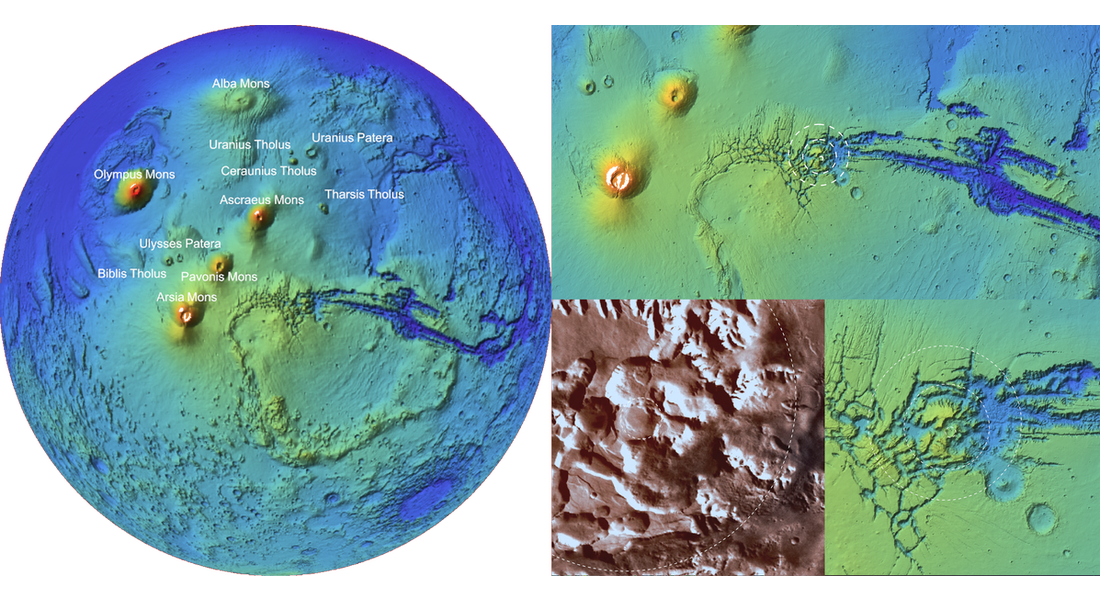
Geography on Celestial Bodies
Construct faithful representations of the geography of Earth’s Moon or the solid planets using satellite imagery or elevation data. Apply the full suite of computation and visualization tools available for Earth geography to planetary geography.
Wolfram Astronomy Documentation
Wolfram Astronomy is an integrated part of Wolfram Language. The full system contains over 6,000 built-in functions covering all areas of computation—all carefully integrated so they work perfectly together.
Full Scope & Documentation
 Guide
Guide Guide
Guide Guide
GuideWolfram Astronomy Q&A
Which Wolfram Language function computes the position of astronomical objects?
AstroPosition gives the positions of astronomical entities with respect to a given frame and coordinate system. AstroDistance finds the distance between celestial bodies. AstroAngularSeparation finds the apparent angular separation of celestial objects.
Is Wolfram Astronomy a standalone application?
No, it’s a core part of Wolfram Language, which means that whether you use Mathematica or the Wolfram Cloud, you can access the astronomy capabilities along with the rest of Wolfram’s computation, visualization and data features.
How does Wolfram compare to other astronomy software?
Wolfram Astronomy integrates with the full functionality of Wolfram Language, including precise computation and extensive visualization. Other systems are either astronomy only or require nontrivial installation of additional packages.
How can I create visualizations of astronomical events?
Use AstroGraphics to show a map of any region of the sky, as viewed on any date from anywhere in the solar system. It can show celestial objects and named constellations. FindAstroEvent gives the dates of events.
When is the next solar eclipse?
The function SolarEclipse uses the DE440 ephemerides from NASA, spanning a period of more than 30 millennia from approximately –13200 to 17200, to calculate dates and other properties of eclipses.
How do I plot historical data for moon phases?
Use the function MoonPhase to find the Moon's fraction of illumination on a specified date. You can get the name of the phase, show it as an icon or plot the value for a range of dates.
+ See More Q&As
How can I customize a map of the Apollo Moon landing sites?
See Map the Lunar Landing Location of Apollo Missions for an example that uses the Wolfram Knowledgebase to get the Apollo landing site locations and plot them on a map of the Moon.
Does Wolfram Astronomy use the newest JPL ephemerides?
Yes, the Wolfram system includes the latest releases of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory Development Ephemerides, DE440 and DE441.