구형 메르카토르와 타원형 메르카토르
메르카토르 도법은 지구의 구형 모델 사용 경우와 타원형 모델 사용 경우에 따라 다른 결과를 도출해 냅니다. Wolfram 언어는 두 경우 모두 사용할 수 있습니다.
대부분의 지도 웹 서버에서 사용되는 투영법은 지구의 구형 모델이며, 이는 "웹 메르카토르"라 불립니다.
In[1]:=
webMercator = {"Mercator",
"ReferenceModel" -> GeodesyData["WGS84", "SemimajorAxis"]}Out[1]=
In[2]:=
ellipMercator = {"Mercator", "ReferenceModel" -> "WGS84"}Out[2]=
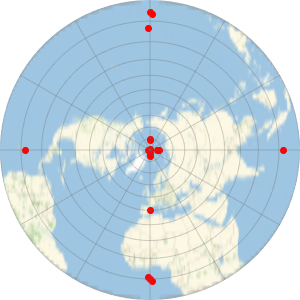
두 도법을 사용하여 옥스포드 대학의 위치를 변환합니다.
In[3]:=
p = GeoPosition[
Entity["University", "UniversityOfOxfordUnitedKingdom36022"]]Out[3]=
In[4]:=
GeoGridPosition[p, webMercator][[1]]Out[4]=
In[5]:=
GeoGridPosition[p, ellipMercator][[1]]Out[5]=
지도에서 33km 이상에 상당하는 수직 방향의 차이를 볼 수 있습니다.
In[6]:=
GeoGridPosition[p, webMercator][[1]];
GeoGridPosition[p, ellipMercator][[1]];
%% - %Out[6]=
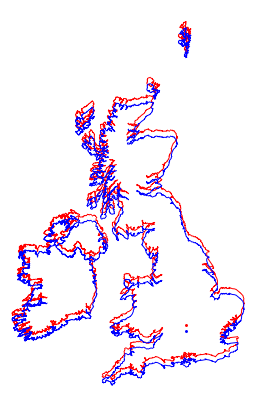
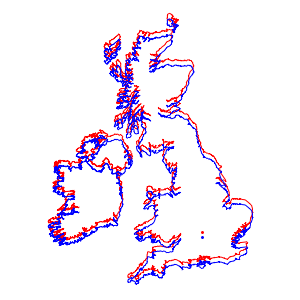
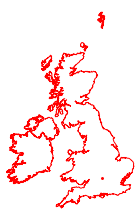
예를 들어, 영국과 아일랜드의 지도를 각각 그릴때, 두 경우 모두 거의 동일하게 나타납니다.
In[7]:=
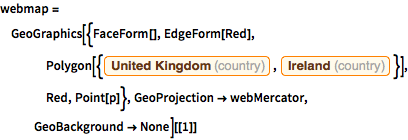
webmap = GeoGraphics[{FaceForm[], EdgeForm[Red],
Polygon[{Entity["Country", "UnitedKingdom"],
Entity["Country", "Ireland"]}], Red, Point[p]},
GeoProjection -> webMercator, GeoBackground -> None][[1]]Out[7]=
In[8]:=

ellipmap =
GeoGraphics[{FaceForm[], EdgeForm[Blue],
Polygon[{Entity["Country", "UnitedKingdom"],
Entity["Country", "Ireland"]}], Blue, Point[p]},
GeoProjection -> ellipMercator, GeoBackground -> None][[1]]Out[8]=
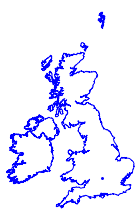
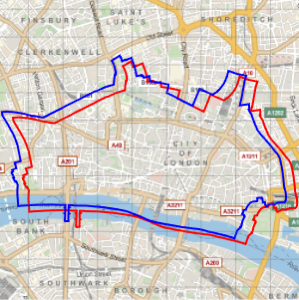
하지만, 하나의 지도에 겹쳐보면 그 차이를 명확히 알 수 있습니다.
In[9]:=
Show[webmap, ellipmap]Out[9]=