Resolva a equação da onda usando sua solução fundamental
Defina um operador de onda em uma dimensão espacial.
In[1]:=
waveOperator = \!\(
\*SubscriptBox[\(\[PartialD]\), \({t, 2}\)]\(u[x, t]\)\) - \!\(
\*SubscriptBox[\(\[PartialD]\), \({x, 2}\)]\(u[x, t]\)\);Obtenha a solução fundamental usando GreenFunction.
In[2]:=
gf[x_, t_, y_, s_] =
GreenFunction[waveOperator, u[x, t], {x, -\[Infinity], \[Infinity]},
t, {y, s}]Out[2]=
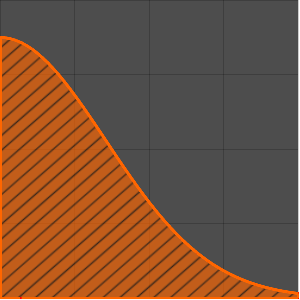
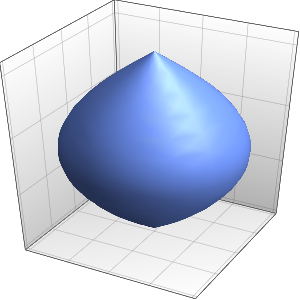
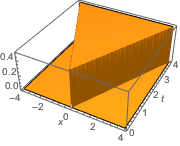
Faça uma representação gráfica da solução fundamental.
In[3]:=
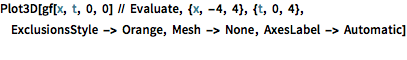
Plot3D[gf[x, t, 0, 0] // Evaluate, {x, -4, 4}, {t, 0, 4},
ExclusionsStyle -> Orange, Mesh -> None, AxesLabel -> Automatic]
Out[3]=
Defina uma função que representa um termo fonte.
In[4]:=
f[y_, s_] := Cos[y] E^(-s)Resolva a equação da onda com este termo forçado através do cálculo da integral de convolução 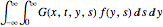 .
.
In[5]:=
sol = Integrate[
gf[x, t, y, s] f[y, s], {y, -\[Infinity], \[Infinity]}, {s,
0, \[Infinity]}, Assumptions -> t > 0 && Im[x] == 0] //
FullSimplifyOut[5]=
Obtenha o resultado usando DSolveValue com condições iniciais homogeneas.
In[6]:=
initialc = {u[x, 0] == 0, Derivative[0, 1][u][x, 0] == 0};In[7]:=
DSolveValue[{waveOperator == f[x, t], initialc}, u[x, t], {x, t}]Out[7]=
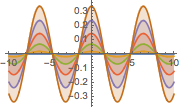
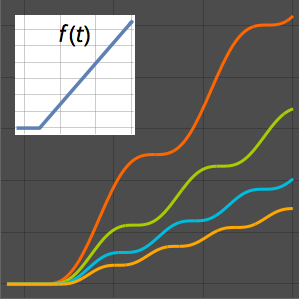
Visualize a onda estacionária gerada pela solução.
In[8]:=
Plot[Table[sol, {t, 0, 1, 0.2}] // Evaluate, {x, -10, 10},
Filling -> Axis]Out[8]=